Table of Contents
Unit 1 | Algebra
Page 1 | Expressions and Formulae
Page 3| Solving Linear Equations
Page 4| Expanding and Factorising
Page 5| Factorising Quadratics and expanding double brackets
Page 6| Patterns and Sequences
Page 7| Simultaneous Equations
Page 8| Changing the subject of a Formula
Page 9| Adding , subtracting algebraic formulas
Unit 2 |Graphs
Page 1 | Straight line graphs
Page 2 | Graphs of Quadratic functions
Unit 3 |Geometry and Measure
Page 2 | Symmetry
Page 3 | Coordinates
Page 4 | Perimeter, Area, Volume
Page 6 | Measurement
Page 7 | Trigonometry
Page 8 | Pythagoras
Page 9 | Angles
Page 10 | Shapes
Page 11| Time
Page 12 | Locus
Unit 4 | Numbers
Page 1 | Speed, Distance and time
Page 2 | Rounding and estimating
Page 3 | Ratio and proportion
Page 4 | Factors, Multiples and primes
Page 5 | Powers and roots
Page 7 | Positive and negative numbers
Page 8 | Basic operations
Page 9 | Fractions
Page 10 | Percentages
Unit 5 | Statistics and Probability
Page 1 | Sampling data (MA)
Page 2 | Recording and representing data
Page 3 | Mean median range and mode
Page 4 | Standard deviation
Unit 4 | Calculus
Using Units of Measurement
- It’s important to use the correct unit of measurement when estimating the length, mass or capacity of something.
- When estimating quantities of an object you don’t know, try to think of some familiar objects that you know and compare them. For example, if you know that an average-sized pear is 100g, then if you had a peach of a similar size, you’d know that its size should be measured in grams.
Equipment for measuring
1. For measuring length, we usually use a ruler of some sort. For larger lengths, there are ‘rolling rulers’
2.For measuring mass, we can use weighting scales of different sizes.
3.For measurng capacities, we can use measuring cylinders or measuring jugs.
Reading measurments
- When reading measurements, it is important that you first take a look at the units of the equipment and how much each division is worth.
- You can then count up until you reach the marker.
1)
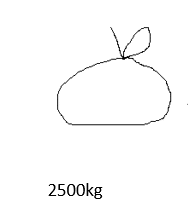
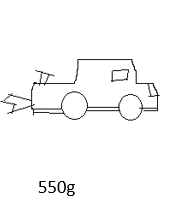
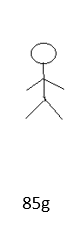
Match the corresponding mass to the diagrams.
2)
a) baby was weight at 3.8kg,Draw an arrow pointing to thecorrectmass.
b) The baby loses 300g in weight .Draw an arrow to the new weight .
3)
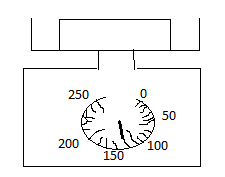 a) Francis has weighed outsome butter on some kitchen scales. How many grams does the butter weigh.g
a) Francis has weighed outsome butter on some kitchen scales. How many grams does the butter weigh.g ![]() (135g)
(135g)
b) How many ounces does the butter weigh ![]() (30g i102)
(30g i102)
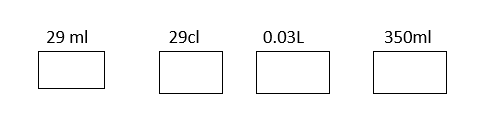
4) Order these from smallest to largest